Security & Privacy
Why Security Is Crucial in the World of Crypto: Protecting Your Digital Assets

|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|

Why Security Is Crucial in the World of Crypto
The world of cryptocurrency offers immense opportunities for financial growth, innovation, and decentralization. However, with these benefits comes a significant challenge: security risks. In an industry where transactions are irreversible and digital assets are stored online, security is crucial in the world of crypto. Without proper safeguards, investors and users risk losing their funds to hacks, scams, and other malicious activities.
In this article, we’ll explore why security matters so much in crypto, examine real-world examples of breaches, and provide actionable tips to protect your digital assets. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or new to the space, understanding these principles will help you navigate the crypto ecosystem safely.
The Growing Importance of Security in Crypto
As the adoption of cryptocurrencies accelerates, so do the threats targeting the industry. According to a 2023 report by Chainalysis, hackers stole over $3.8 billion worth of crypto in 2022 alone. These figures highlight the urgent need for robust security measures.
Why Security Matters:
- Irreversible Transactions: Unlike traditional banking systems, crypto transactions cannot be reversed once completed.
- Decentralized Nature: While decentralization empowers users, it also means there’s no central authority to recover lost funds.
- High Value of Assets: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum hold significant value, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Without prioritizing security, even experienced users can fall victim to attacks.
Common Security Threats in the Crypto Space
Understanding the risks is the first step toward mitigating them. Below are some of the most prevalent threats in the crypto world:
1. Hacks and Exchange Breaches
Cryptocurrency exchanges are prime targets for hackers due to the large amounts of funds they hold. Notable incidents include:
- Mt. Gox (2014): Over 850,000 BTC were stolen, leading to the collapse of the exchange.
- FTX Collapse (2022): Mismanagement and alleged fraud resulted in billions of dollars in losses.
Key Takeaway:
Centralized exchanges are convenient but vulnerable. Always transfer your holdings to secure wallets after purchasing.
2. Phishing Scams
Scammers often impersonate legitimate platforms or individuals to steal login credentials and private keys.
- Example: Fake websites mimicking popular exchanges trick users into entering sensitive information.
3. Malware and Ransomware
Malicious software can infiltrate devices to steal crypto wallets or demand ransoms.
- Tip: Avoid downloading files or clicking links from unknown sources.
4. Social Engineering Attacks
These involve manipulating users into revealing private information.
- Case Study: The 2020 Twitter hack compromised high-profile accounts to promote a Bitcoin scam.
5. Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Decentralized applications (dApps) built on blockchains like Ethereum can have coding flaws that hackers exploit.
- Example: The 2022 Wormhole bridge hack resulted in a $320 million loss due to a smart contract bug.
Real-World Consequences of Poor Security
Ignoring security in crypto can lead to devastating outcomes. Here are some sobering examples:
1. Ronin Network Hack (2022)
Hackers exploited a vulnerability in the Ronin bridge, stealing $625 million in Ethereum and USDC. This incident highlighted the risks of relying on poorly audited infrastructure.
2. Individual Losses
Many users lose funds due to simple mistakes, such as sharing private keys or falling for phishing scams. A single error can result in permanent loss.
3. Regulatory Scrutiny
Security breaches often attract regulatory attention, leading to stricter rules that impact the entire industry.
Best Practices for Enhancing Crypto Security
Protecting your assets requires a proactive approach. Follow these practical tips to safeguard your investments:
1. Use Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets, such as Ledger and Trezor, store private keys offline, making them immune to online attacks.
- Why It Works: Even if your computer is compromised, your funds remain secure.
For more details, visit Ledger’s official site.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Add an extra layer of protection to your accounts by enabling 2FA. Use authenticator apps instead of SMS-based codes, which are vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks.
3. Secure Your Private Keys
- Never share your private keys or seed phrases with anyone.
- Store them offline in a safe location, such as a fireproof safe or encrypted USB drive.
4. Verify Website URLs
Always double-check URLs before entering sensitive information. Bookmark trusted sites to avoid phishing attempts.
5. Keep Software Updated
Regularly update your wallets, apps, and antivirus software to patch vulnerabilities.
6. Be Wary of Unsolicited Offers
Avoid deals that seem too good to be true, especially those involving “guaranteed returns” or “free tokens.”
7. Audit Smart Contracts
If you’re investing in DeFi projects, ensure their smart contracts have been audited by reputable firms like CertiK or OpenZeppelin.
For more on smart contract audits, check out CertiK’s website.
The Role of Education in Crypto Security
Knowledge is one of the most powerful tools for staying safe in the crypto world. Educate yourself on:
- How blockchain technology works.
- Common scams and red flags to watch for.
- Secure practices for storing and transferring crypto.
Recommended Resources:
- Websites: CoinDesk, CryptoSlate.
- Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer beginner-friendly crypto courses.
- Communities: Join forums like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency for peer advice.
The Future of Security in Crypto
As the industry matures, advancements in security technology are emerging to combat threats:
- Multi-Signature Wallets: Require multiple approvals for transactions, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Enable privacy-focused transactions without compromising security.
- AI and Machine Learning: Detect anomalies and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time.
While these innovations are promising, individual responsibility remains paramount.
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Security to Succeed
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency, security is crucial to protecting your investments and ensuring long-term success. By adopting best practices, staying informed, and leveraging advanced tools, you can minimize risks and enjoy the benefits of this revolutionary technology.
Ready to take action? Start by securing your wallet, auditing your current practices, and educating yourself further. Remember, in crypto, prevention is always better than regret.
Security & Privacy
Why Cold Wallets Are Safer Than Hot Wallets?


Why Cold Wallets Are Safer Than Hot Wallets
Introduction
In the world of cryptocurrencies, securing your digital assets is paramount. As the market continues to evolve, so do the methods of storage available to crypto holders. Among these, two primary categories stand out: hot wallets and cold wallets. In this article, we will explore why cold wallets are safer than hot wallets, examining their functionality, security measures, and practical applications in safeguarding your digital wealth.
Understanding Hot Wallets
What Are Hot Wallets?
Hot wallets are online wallets connected to the internet, providing users with quick access to their cryptocurrencies. These wallets are often integrated into exchanges and mobile applications, making transactions easy and immediate. Examples include software wallets on your phone or desktop, as well as web wallets accessed through browsers.
Advantages of Hot Wallets
- Convenience: Hot wallets enable quick and easy transactions, perfect for regular trading and everyday use.
- Accessibility: Users can access their funds from anywhere, anytime, provided they have an internet connection.
- User-Friendly: Most hot wallets have intuitive interfaces, making them accessible to beginners.
Disadvantages of Hot Wallets
- Security Risks: Being connected to the internet exposes hot wallets to vulnerabilities such as hacking, phishing attacks, and malware.
- Custodial Risks: If you keep your assets on an exchange, you rely on their security protocols, which may not always be robust.
Understanding Cold Wallets
What Are Cold Wallets?
Cold wallets, on the other hand, are offline storage solutions that are not connected to the internet. They can be in the form of hardware wallets or paper wallets. By keeping your private keys offline, cold wallets significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Advantages of Cold Wallets
- Enhanced Security: The main reason why cold wallets are safer than hot wallets is their offline nature, which makes them immune to online threats.
- Reduced Risk of Loss: With proper management, your assets are less likely to be lost to hacks or breaches.
- Long-Term Storage: Cold wallets are ideal for long-term holders who do not require frequent access.
Disadvantages of Cold Wallets
- Less Convenience: Accessing funds from a cold wallet requires more steps, making it less ideal for day-to-day transactions.
- Physical Risks: Cold wallets can be lost or damaged; therefore, proper backup and storage practices are essential.
Why Cold Wallets Are Safer Than Hot Wallets
1. Offline Storage Equals Enhanced Security
Cold wallets store your private keys offline. This absence of internet connectivity means that hackers and malicious software have no pathway to your funds. Even if a user inadvertently downloads malware or falls victim to phishing schemes, their cold wallet remains unaffected.
2. Control Over Your Private Keys
When you use a hot wallet, you often rely on third-party services to manage your private keys. This factor introduces additional risk, as your assets are only as safe as the provider’s security protocols. In contrast, cold wallets give you complete control over your private keys, ensuring that only you can access your assets.
3. Protection Against Exchange Vulnerabilities
Cryptocurrency exchanges are frequent targets for hackers. Many high-profile breaches have resulted in significant losses for users. By keeping your assets in a cold wallet rather than on an exchange, you minimize risk. Even if an exchange suffers a breach, your assets remain secure in your cold wallet.
4. Less Constant Interaction with the Internet
The less frequently a wallet interacts with the internet, the lesser the risk of exposure to cyber threats. This fundamentally speaks to why cold wallets are safer than hot wallets. When using cold storage, funds remain untouched unless you explicitly choose to move them, greatly limiting potential attack vectors.
When to Use Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets
Ideal Use Cases for Hot Wallets
- Frequent Traders: If you actively trade cryptocurrencies, hot wallets offer the quick access necessary for timely transactions.
- Small Amounts: For everyday access and small quantities of cryptocurrencies that you can afford to lose, hot wallets suffice.
Ideal Use Cases for Cold Wallets
- Long-Term Holders: If you aim to hold your assets for an extended period, cold wallets are the best option for security.
- Large Amounts: Investors holding significant amounts of cryptocurrency should prioritize cold storage to safeguard against theft.
Actionable Tips for Wallet Security
- Research Wallet Options: Choose reputable cold wallets with strong security features.
- Backup Your Wallet: Always create backups of your cold wallet and keep them in secure locations.
- Keep Your Software Updated: For hot wallets, ensure that your software is always up-to-date to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Use Two-Factor Authentication: For added security in hot wallets, enable two-factor authentication.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest threats in the cryptocurrency space to protect your assets.
Conclusion
Understanding why cold wallets are safer than hot wallets is essential to securing your cryptocurrency investments. While hot wallets provide convenience, their online nature introduces vulnerabilities that can be avoided with cold storage. For anyone serious about cryptocurrency security, opting for cold wallets is a crucial step in safeguarding your financial future.
Call to Action
Are you ready to enhance the security of your digital assets? Start exploring cold wallets today and safeguard your cryptocurrency investments for the future.
Security & Privacy
Mitigating Quantum Threats to Blockchain Security


Mitigating Quantum Threats to Blockchain Security
Introduction
As the digital landscape evolves, so too do the threats faced by blockchain technology. Among the most significant is the risk posed by quantum computing—a new breed of technology that could render current cryptographic protocols ineffective. This article delves deep into understanding these quantum threats to blockchain security and explores actionable strategies to mitigate them. We’ll also examine advanced technical concepts, emerging trends, and the role of cutting-edge technologies in securing blockchain systems against quantum adversaries.
Understanding the Quantum Threat
What Are Quantum Computers?
Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, to process information in ways that classical computers cannot. Unlike classical bits, which can either be 0 or 1, qubits (quantum bits) can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This unique capability provides quantum computers with immense processing power, enabling them to solve certain problems exponentially faster than classical systems.
While today’s quantum computers are still in their infancy, rapid advancements suggest that quantum supremacy—the point at which quantum computers outperform classical ones for specific tasks—will soon become a reality. This poses a significant threat to cryptographic systems, including those underpinning blockchain technology.
How Quantum Computers Threaten Blockchain Security
Blockchain security relies on robust cryptographic protocols to ensure data integrity, user anonymity, and immutability. The advent of powerful quantum computers introduces several critical vulnerabilities:
1. Breaking Public-Key Cryptography
Public-key cryptography, which secures blockchain transactions and wallets, relies on mathematical problems like integer factorization (used in RSA) and elliptic curve discrete logarithms (used in ECC). Quantum computers can execute algorithms like Shor’s algorithm, which solves these problems exponentially faster than classical algorithms. If compromised, public-key encryption would leave blockchain transactions vulnerable to interception and manipulation.
2. Tampering with Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) rely on cryptographic puzzles and randomness to validate transactions and maintain network integrity. Quantum computers could exploit weaknesses in these mechanisms:
- In PoW, quantum computers could solve hashing puzzles significantly faster, gaining disproportionate control over block creation.
- In PoS, quantum attacks could compromise private keys, allowing attackers to manipulate voting power and alter transaction history.
3. Stealing Private Keys
Quantum computers could theoretically derive private keys from public keys using algorithms like Grover’s algorithm, which accelerates brute-force searches. This would enable attackers to compromise wallets and private transactions, undermining trust in blockchain systems.
4. Threatening Data Integrity
Quantum adversaries could retroactively decrypt historical blockchain data, exposing sensitive information and violating privacy guarantees. This is particularly concerning for blockchains used in industries like healthcare and finance.
Strategies for Mitigating Quantum Threats
To secure blockchain systems against quantum threats, the industry must adopt a proactive and multi-layered approach. Below are detailed strategies to consider:
1. Transitioning to Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
The cornerstone of mitigating quantum threats is adopting cryptographic algorithms designed to withstand quantum attacks. These include:
a. Lattice-Based Cryptography
Lattice-based cryptography relies on the hardness of solving lattice problems, which are believed to be resistant to both classical and quantum attacks. Examples include:
- Kyber: A key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) standardized by NIST for post-quantum cryptography.
- Dilithium: A digital signature algorithm offering high security and efficiency.
b. Hash-Based Cryptography
Hash-based signatures, such as SPHINCS+, use cryptographic hash functions to create secure signatures. While slower than traditional methods, they provide strong resistance to quantum attacks.
c. Code-Based Cryptography
Code-based cryptography, exemplified by McEliece, leverages error-correcting codes to secure data. It has withstood decades of cryptanalysis and remains a promising candidate for post-quantum security.
d. Multivariate Polynomial Cryptography
This approach uses systems of multivariate quadratic equations to create cryptographic schemes. While less mature than other methods, it offers potential for lightweight applications.
Active Participation in Research
Engage with organizations like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which is actively standardizing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms. Staying informed about these developments ensures timely adoption of quantum-resistant solutions.
2. Enhancing Security Protocols
In addition to transitioning to quantum-resistant cryptography, blockchain systems must strengthen existing security protocols:
a. Multi-Signature Approaches
Implement multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets, where multiple parties must validate a transaction. This adds redundancy and makes it harder for quantum attackers to compromise all required private keys.
b. Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Adopt zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), which allow one party to prove knowledge of a secret without revealing it. ZKP-based protocols like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs enhance privacy and security, even in a quantum-threatened environment.
c. Regular Security Audits
Conduct periodic audits of blockchain systems to identify vulnerabilities and enhance security protocols. Use tools like static analysis and penetration testing to simulate quantum attacks and evaluate system resilience.
3. Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about quantum threats is crucial for fostering a culture of security:
a. Training for Developers
Equip blockchain developers with knowledge about quantum computing and its implications for security. Offer workshops, certifications, and resources on post-quantum cryptography.
b. Public Awareness
Educate users about quantum risks and encourage them to adopt best practices, such as regularly updating wallets and avoiding exposure of public keys.
4. Collaboration Within the Industry
Collaboration is essential for addressing quantum threats effectively:
a. Inter-Blockchain Cooperation
Encourage collaboration between different blockchain networks to share insights and develop collective security measures. For example, interoperability protocols like Polkadot and Cosmos can facilitate joint efforts.
b. Research Partnerships
Establish partnerships between academia, industry, and government to advance research in quantum-secure technologies. Initiatives like the Quantum Internet Alliance demonstrate the value of cross-sector collaboration.
5. Migration and Upgrades
Plan for a smooth transition to quantum-resistant systems:
a. Roadmap for Implementation
Blockchain projects should develop a roadmap for integrating quantum-resistant features. This includes:
- Testing new algorithms in sandbox environments.
- Gradually phasing out vulnerable protocols.
b. Monitoring Quantum Computing Developments
Stay informed about advancements in quantum computing through platforms like IBM Quantum, Google Quantum AI, and Microsoft Azure Quantum. Anticipate necessary adaptations in security protocols based on emerging capabilities.
Advanced Concepts in Quantum-Resistant Blockchain Security
1. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
QKD uses quantum mechanics to securely distribute encryption keys. By leveraging the principle of quantum entanglement, QKD ensures that any eavesdropping attempt is detectable, making it an ideal solution for securing blockchain communications.
2. Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it. This enhances privacy and security, even in the presence of quantum adversaries.
3. Decentralized Quantum Networks
Future blockchain systems could integrate decentralized quantum networks to enhance security. These networks would use quantum nodes to validate transactions and prevent tampering.
4. Hybrid Cryptographic Systems
Hybrid systems combine classical and quantum-resistant algorithms to provide layered security. For example, a blockchain could use ECC for short-term security and lattice-based cryptography for long-term protection.
Current Trends and Future Perspectives
According to a recent Gartner report, around 75% of organizations believe quantum computing will offer a distinct advantage within the next few years. Early adopters of quantum-resistant solutions will likely gain a competitive edge, while laggards risk falling victim to quantum attacks.
Key trends shaping the future of blockchain security include:
- Increased investment in post-quantum cryptography research.
- Development of quantum-resistant hardware wallets.
- Integration of AI-driven anomaly detection to identify quantum threats.
Key Takeaways
Mitigating quantum threats to blockchain security requires a fundamental shift in how we design and implement blockchain systems. Here are the key takeaways:
- Invest in Quantum-Resistant Technologies: Early adoption of post-quantum cryptographic algorithms is essential for safeguarding blockchain systems.
- Stay Updated on Quantum Advances: Monitor advancements in quantum computing to anticipate and address emerging threats.
- Foster Collaboration: Collaborate across industries to build robust defenses against quantum adversaries.
- Plan for Migration: Develop a clear roadmap for transitioning to quantum-resistant protocols.
Call to Action
Now is the time for blockchain developers, businesses, and users to take proactive steps in addressing quantum threats. Start by researching quantum-resistant strategies and integrating them into your blockchain initiatives. Stay informed, stay prepared, and protect your data, assets, and identities in the age of quantum computing.
Security & Privacy
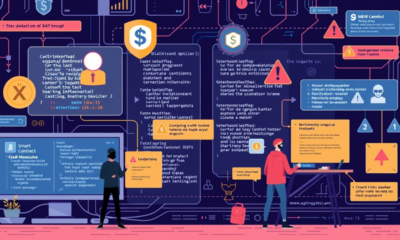
Developing Incident Response Plans for Crypto Breaches: A Comprehensive Guide


Developing Incident Response Plans for Crypto Breaches
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, security breaches have become increasingly sophisticated and devastating. From exchange hacks to wallet compromises, the crypto industry faces unique challenges that require specialized incident response strategies. As digital assets continue to gain mainstream adoption, organizations handling cryptocurrencies must develop robust incident response plans that address the specific nuances of blockchain technology and crypto assets.
This comprehensive guide explores the essential components of an effective incident response plan for cryptocurrency breaches, providing actionable insights for exchanges, wallet providers, DeFi platforms, and individual investors alike.
The Rising Threat Landscape for Crypto Assets
The cryptocurrency sector has witnessed numerous high-profile security incidents in recent years. In 2023 alone, crypto-related hacks resulted in losses exceeding $3.9 billion, according to Chainalysis data. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology, while revolutionary, presents unique security challenges that traditional incident response frameworks may not adequately address.
Common cryptocurrency security threats include:
- Smart contract vulnerabilities and exploits
- Private key compromises
- Phishing attacks targeting exchange credentials
- Social engineering schemes
- 51% attacks on smaller blockchains
- API vulnerabilities in custodial services
- Flash loan attacks in DeFi protocols
Key Components of a Crypto-Specific Incident Response Plan
1. Preparation Phase
Effective incident response begins long before a breach occurs. The preparation phase involves:
Risk Assessment and Asset Inventory
Conduct a thorough inventory of all crypto assets, including:
- Types of cryptocurrencies held
- Storage methods (hot wallets, cold storage, custodial services)
- Access control mechanisms
- Smart contract dependencies
- Third-party service integrations
Establish a Dedicated Incident Response Team
Your IR team should include members with specialized expertise in:
- Blockchain forensics
- Smart contract security
- Cryptographic principles
- Regulatory compliance
- Public communications
Documentation and Communication Protocols
Develop clear documentation covering:
- Escalation procedures
- Decision-making authority during incidents
- Communication templates for stakeholders
- Regulatory reporting requirements
- Chain of custody procedures for evidence
2. Detection and Analysis
Early detection can significantly reduce the impact of cryptocurrency breaches. Implement robust monitoring systems to identify suspicious activities:
Transaction Monitoring
Deploy analytics tools that can detect:
- Unusual transaction patterns or volumes
- Transactions to known malicious addresses
- Unexpected withdrawals from cold storage
- Suspicious smart contract interactions
Blockchain Forensics Capabilities
Establish relationships with blockchain analytics firms or develop in-house capabilities to:
- Trace fund movements across blockchains
- Identify mixed or tumbled transactions
- Monitor darknet markets for stolen assets
- Analyze transaction graphs for suspicious patterns
Automated Alert Systems
Implement automated monitoring with adjustable thresholds for:
- Large or unusual transactions
- Multiple failed authentication attempts
- Suspicious API calls or RPC requests
- Smart contract anomalies
3. Containment Strategies
When a breach is detected, swift containment is critical to minimize losses:
Immediate Response Actions
Develop protocols for:
- Temporarily suspending trading/withdrawals
- Freezing affected wallets
- Isolating compromised nodes or systems
- Deploying circuit breakers for DeFi protocols
On-Chain Mitigation Techniques
Establish procedures for:
- Emergency upgrade of vulnerable smart contracts
- Implementing pause functions in protocols
- Coordinating with miners/validators for potential chain rollbacks (in extreme cases)
- Whitelisting capabilities to prevent further unauthorized transfers
Coordination with External Parties
Develop relationships with:
- Exchanges to block/flag stolen funds
- Law enforcement agencies with crypto expertise
- Blockchain forensics companies
- Industry response groups
4. Eradication and Recovery
After containing the breach, focus on eradicating vulnerabilities and recovering operations:
Vulnerability Remediation
Develop procedures for:
- Patching identified vulnerabilities
- Updating key management systems
- Conducting thorough security audits
- Implementing improved security controls
Asset Recovery Strategies
Establish protocols for:
- Working with exchanges to recover stolen funds
- Negotiating with attackers (when appropriate)
- Implementing compensation plans for affected users
- Insurance claims processing
Secure Resumption of Operations
Create detailed checklist for:
- Gradual restoration of services
- Enhanced monitoring during recovery
- Verification procedures for system integrity
- Phased approach to re-enabling withdrawals
5. Post-Incident Activities
Learning from security incidents is crucial for preventing future breaches:
Comprehensive Incident Documentation
Document all aspects of the incident:
- Attack vectors and methodologies
- Timeline of events
- Actions taken and their effectiveness
- Evidence collected for potential legal proceedings
Root Cause Analysis
Conduct thorough investigation to determine:
- Initial entry points
- Security gaps exploited
- Missed warning signs
- Effectiveness of detection systems
Updating Response Procedures
Revise incident response plans based on:
- Lessons learned
- New threat intelligence
- Regulatory developments
- Industry best practices
Regulatory Considerations for Crypto Incident Response
Cryptocurrency breaches often trigger regulatory reporting requirements across multiple jurisdictions. Your incident response plan should address:
Reporting Obligations
- Financial authorities (FinCEN, SEC, CFTC in the US)
- Data protection regulators (GDPR in Europe)
- Law enforcement agencies
- Securities regulators for tokenized assets
Documentation Requirements
Maintain detailed records for:
- Breach timeline and scope
- Affected assets and customers
- Response actions taken
- Remediation measures implemented
Customer Communication
Develop templates for:
- Initial breach notifications
- Status updates during investigation
- Final incident reports
- Compensation information
Specialized Tools for Crypto Incident Response
Several specialized tools can enhance cryptocurrency incident response capabilities:
Blockchain Analytics Platforms
Tools like Chainalysis, Elliptic, and TRM Labs provide:
- Transaction tracing across multiple blockchains
- Address clustering and entity identification
- Risk scoring for suspicious transactions
- Visualization of fund flows
Threat Intelligence Services
Crypto-specific threat intelligence services offer:
- Early warning of emerging threats
- Indicators of compromise
- Known malicious addresses
- Attack pattern identification
Smart Contract Monitoring
Services like Forta Network and OpenZeppelin Defender provide:
- Real-time smart contract monitoring
- Anomaly detection in contract interactions
- Automated response capabilities
- Custom detection bots
Case Studies: Learning from Major Crypto Breaches
The Poly Network Hack (2021)
In August 2021, Poly Network suffered a $611 million hack—one of the largest in DeFi history. Their response demonstrated both strengths and weaknesses:
Strengths:
- Quick public communication established transparency
- Direct communication with the attacker led to full fund recovery
- Comprehensive technical post-mortem increased industry awareness
Weaknesses:
- Initial vulnerability went undetected despite audits
- Lack of circuit breakers allowed complete drainage of funds
- Cross-chain complexity complicated the response effort
Lessons for Incident Response Plans:
- Implement multiple layers of security monitoring
- Develop communication strategies for engaging with attackers
- Design circuit breakers appropriate for protocol value
- Plan for cross-chain complexity in response strategies
Building a Testing and Simulation Program
Regular testing strengthens incident response capabilities:
Tabletop Exercises
Conduct scenario-based exercises that:
- Test decision-making under pressure
- Validate communication channels
- Identify gaps in response procedures
- Build team coordination
Technical Simulations
Perform regular technical drills including:
- Simulated wallet compromises
- Smart contract exploit scenarios
- Phishing attack simulations
- Recovery from cold storage
Third-Party Assessments
Engage external experts to:
- Conduct penetration testing
- Review incident response procedures
- Simulate advanced persistent threats
- Evaluate blockchain-specific vulnerabilities
Conclusion: Building Resilience in the Face of Crypto Threats
As cryptocurrency adoption continues to grow, the sophistication and frequency of attacks will likely increase. Organizations handling digital assets must develop comprehensive, tested, and continuously improved incident response plans specific to cryptocurrency threats.
The most effective incident response plans combine technical expertise, clear procedures, regular testing, and cross-industry collaboration. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, organizations can significantly reduce the impact of cryptocurrency breaches and build greater trust in their security posture.
Remember that incident response is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process of preparation, detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and learning. Invest in developing these capabilities now to protect your digital assets against the evolving threat landscape.
Call to Action
Don’t wait for a breach to test your cryptocurrency security posture. Begin developing or enhancing your crypto-specific incident response plan today. Start by conducting a risk assessment, forming a dedicated response team, and establishing clear protocols for detection and containment.
For organizations looking to strengthen their cryptocurrency security, consider engaging specialized consultants with blockchain security expertise and joining industry information-sharing groups to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices.
-

 Security & Privacy4 months ago
Security & Privacy4 months agoAdvanced Techniques for Securing Multi-Signature Wallets
-

 Crypto Basics4 months ago
Crypto Basics4 months agoHow to Spot Fake News in the Crypto Space: A Comprehensive Guide for Savvy Investors
-

 Video4 months ago
Video4 months agoTop Mistakes New Investors Make in Crypto
-

 Video4 months ago
Video4 months agoThe Easiest Way to Buy NFTs: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Video4 months ago
Video4 months agoPublic vs Private Blockchain | Difference Between Public and Private Blockchain
-

 Web3 & Metaverse4 months ago
Web3 & Metaverse4 months agoTitle: Implementing Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Web3 Applications: A Comprehensive Guide to Security and Privacy
-

 Investment Strategies4 months ago
Investment Strategies4 months agoPsychological Aspects of Trading: Mastering Emotions for Financial Success
-

 Regulations & Policy Updates4 months ago
Regulations & Policy Updates4 months agoLegal Frameworks for Launching Security Tokens: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025